

lsblk is a great tool for getting disk information. I'd always advise enumerating disks every time before performing operations considered as destructive. Now, assuming we have added another disk or two to our system, we need to enumerate disks detected by Linux.

These tools will come handy and still have use with today's advanced LVM tools such as the System Storage Manager: lsblk, parted, and mkfs.xfs. Traditional Linux Disk Administration Toolsīefore being acquainted with the latest and greatest featured tools for LVM Management in CentOS 7, we should first explore more traditional tools that have been used for Linux disk management. If we have two physical disks of 1TB each, we can create a volume group of almost 2TB amongst the two.įrom the volume group, we can create three logical volumes each of any-size not exceeding the total volume group size. Example: disk /dev/sda is partitioned to include two physical partitions: /dev/sda1 and /dev/sda1 Keep in mind, physical partition is not recommended in most common LVM setups. Seen as a storage facility to the operating systemĪ physical volume will be seen as /dev/sda, /dev/sdb a physical disk that is detected by Linux.Ī physical partition will be a section of the disk partitioned by a disk utility such as fdisk. Understanding each piece of a logical volume is important to manage them. Please study the following table to get a firm grasp of each component. When learning about volume management with LVM, it is easier if we know what each component in LVM is. This works in a similar fashion to RAID 0 striping data across separate disks. Note − Using Logical Volumes actually increases disk I/O when configured correctly. One single disk can even be used for snapshots of Logical Volumes.
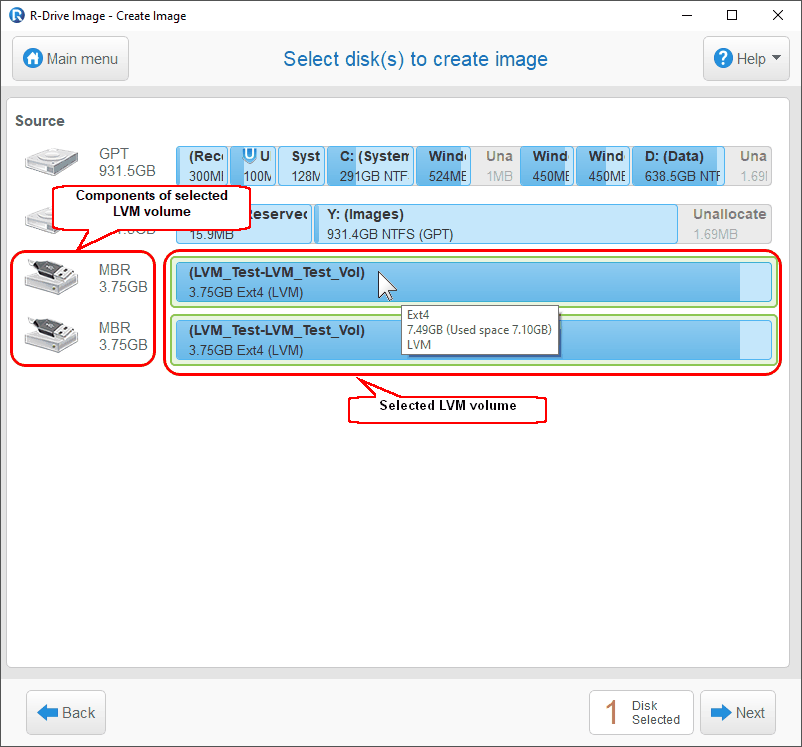
Or even two logical volumes of 1.5TB, 5 volumes of 500GB, or any combination. With LVM, it is possible to have (for example) three physical disks of 1TB each, then a logical volume of around 3TB such as /dev/sdb. However, it can be thought of in a similar concept as RAID 0 or J-Bod. Logical Volume Management (LVM) is a method used by Linux to manage storage volumes across different physical hard disks.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
